Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a typically chronic and systemic autoimmune disease, characterized by the production of a plethora of antibodies directed against ubiquitous self-antigens, then forming the immune complexes (ICs) for which the defect in the clearance make them deposit on the skin, renal, musculoskeletal, and hematopoietic systems contributing to their damage [1]. Its prevalence ranges from 20 to 150 cases per 100,000 population but varies between countries, populations and genders; it predominantly affects women of childbearing age [2, 3]. Although its exact aetiology is not yet well understood, there is no doubt that the genetic factor significantly contributes to its pathogenesis [4, 5] reflected from its familial aggregation [6], twin concordance around 14% in monozygotic (MZ) and 4.4 % in dizygotic (DZ) twins [7], the find of lots of susceptibility genes for SLE [8], inbred mouse strains that consistently develop lupus [9] and hereditary complement component deficiencies (C1s, C2, C4 and C1q) [10].
Recently, the deficiency of C1q comes under the spotlight. C1q is one important component of C1 complex and is produced extrahepatically by many types of cells including monocyte/macrophage, epithelial, dendritic, mesenchymal, microglial, and endothelial cells, as well as fibroblasts and trophoblasts. Structurally, this glycoprotein is assembled from 18 polypeptide chains of three different types named A, B, and C of 29, 27, and 23 kDa resembling a bunch of flowers, with six peripheral globular regions each connected by fibrillary strands to a central bundle of fibres and each of them contains a globular head attached to a collagen-like triple-helix tail, considered as the recognition domain which has ligand binding capability [11]. A, B and C chains which are encoded by separate genes are located at chromosome 1p34.1-36.3. The relevant genes are C1qA (2.5 kb), C1qB (2.6 kb), and C1qC (3.8 kb) and each gene contains two exons separated by one intron [12]. Importantly, the clearance of ICs and apoptotic cell debris call for the involvement of C1q. It is worth mentioning that C1q is considered as a good indicator to diagnose the lupus nephritis (LN) [13], one of fatal complications of SLE patients.
A few populations in SLE-affected families such as Turkey, Sudan, Kosovo and Iraq show that a number of C1q mutations were causative for SLE [14–16]. As confirmed by both animal model and humans, C1q-deficient develops a lupus-like disease and exhibits impaired clearance of apoptotic cells [17, 18]. Furthermore, more than 90% could develop SLE among people with C1q deficiency [19], indicating that the presence of C1q is a protective factor for them from SLE. Specifically, the mutation can result in termination codons, frameshifts or amino acid exchanges. SLE with genetic C1q deficiency is often accompanied by the low level of C1q, the production of low molecular weight C1q with no function and a high level of anti-C1q and it can be due to the mutation of C1q [20, 21], such as rs631090 [22]. In addition, an antibody directing to C1q emerges in about 28–60% of SLE patients and the presence of C1q antibody is linked with disease activity, appearance of renal involvement, especially hypocomplementemia [23–26]. Therefore, some treatment means targeting to C1q is emerging. For instance, restoration of C1q levels by plasma transfusion in C1q-defcient lupus patients resulted in amelioration of the disease [27]. All introductions above disclose that the involvement C1q plays an important role in the development of SLE.
Although several studies have investigated the association between C1q polymorphisms and SLE, results are still considered inconclusive and the sample size is relatively small.
Aim
Therefore, to draw a more comprehensive estimation of the association between C1q and SLE risk, we conducted this meta-analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA) to evaluate the effects of C1q polymorphisms on SLE susceptibility.
Material and methods
Search strategy
A systematic search from PubMed, Web of Science, and CNKI was conducted with the following key words: (“systemic lupus erythematosus” or “SLE”) and (“C1q” or “complement component 1q”) and (“SNP” or “polymorphism” or “single nucleotide polymorphism”). Each database was thoroughly scanned until June 2020. Except that, manual search of reference lists was further performed.
Study selection and data abstraction
Studies included in the current meta-analysis should satisfy the following inclusion criteria: (1) involving the disease risk of C1q polymorphism with SLE; (2) sufficient data of cases and controls to estimate the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) based on the genetic model contrast; (3) individual for all selected samples met the ACR. Major exclusion criteria were limited to several items as follows: (1) overlapping subjects in several articles for the same research group; (2) only focused on family individuals rather than sporadic advanced SLE patients; (3) abstract from conferences, letters, review articles and case reports. The following items obtained from each eligible article included: the first author, the year of publication, journal, country, sample size, genotyping methods and distribution in case and control groups. Data from the retrieved studies were extracted independently by two reviewers. If any disagreement still existed, the third author would be invited to chew over current controversy and resolve the dispute.
Trial sequential analysis
Using TSA software version 0.9 beta (Copenhagen Trial Unit, Copenhagen, Denmark), TSA was performed to prevent the risk of random error (false positive or false negative outcomes) and multiplicity phenomenon due to sparse data and repetitive testing in meta-analyses, to calculate the required meta-analysis information size and to adjust significance thresholds based on a two-sided sequential analysis-adjusted fixed effects model by taking a relative risk reduction (RRR) 20%, power 80% and type I error (α) 5% [28, 29]. The monitoring boundaries were constructed as a way to determine whether the present meta-analysis is sufficiently powered and conclusive. If the Z-curve crosses the TSA boundaries or futility area, it is classified as “firm evidence of effect”; if the Z-curve does not cross any of the boundaries or reached the required information size (RIS), evidence is regarded as “potentially spurious evidence of effect” [30].
Trim and fill method
Trim and fill method was proposed by Duval and Tweedie, and aims at identifying and correcting funnel plot asymmetry caused by publication bias, applying to small study effects. The application significance of this method is to compare whether the pooled effect has changed before and after trimming and filling. If the estimated value of the combined effect does not change significantly, it indicates that the publication bias has little influence and the results are relatively robust.
Statistical analysis
The genetic strength association including pooled ORs and 95% CIs was assessed using different genetic models, including allele model (M vs. m), homozygote model (MM vs. mm), heterozygote model (Mm vs. mm), dominant (MM + Mm vs. mm), recessive (MM vs. Mm + mm), based on allele and genotype frequency of each C1q polymorphic site between cases and healthy controls. In addition, m represents mutant type and M is wild type. The χ2 test was used to estimate whether the control subjects are in line with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE). Cochran’s Q statistic and I 2 statistic were performed to evaluate the heterogeneity assumption between studies. In addition, the random-effect model was utilized in all model analysis. Potential publication bias was evaluated by Egger’s test and trim and fill method. STATA 12.0 software (Stata Corp LP, College Station, Texas, USA) was used to carry out all statistical analysis; p < 0.05 was used to determine statistical significance with two-sided p-values.
Results
Studies included in the meta-analysis
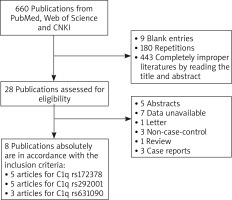
As shown in Figure 1, 660 articles were retrieved completely and systemically from PubMed, Web of Science and CNKI according to search strategy. However, only 28 articles were potentially chosen to assess its eligibility after removing 9 blank entries, 180 repetitions and 443 completely improper articles by reading its title and abstract. Based on the exclusion criteria, 5 abstracts, 7 studies with unavailable data, 1 letter, 3 non-case-control, 1 review and 3 case reports were excluded. Finally, a total of 8 articles [22, 31–37] were included in the current meta-analysis. Among them, 5 articles were for C1q rs172378, 5 articles for C1q rs292001, and 3 articles for C1q rs631090. Detailed information about them was listed in Table 1.
Table 1
Detailed information of the articles included in this meta-analysis
| Author | Year | Journal | Country | Method | Sample size(case/control) | Genotype(case/control) | Allele(case/control) | HWE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | Mm | MM | m | M | ||||||||
| rs172378 | Irshaid FI [31] | 2018 | Pak J Biol Sci | African American | PCR-RFLP | 55/59 | 5/6 | 25/23 | 25/30 | 35/35 | 75/83 | Yes |
| Irshaid FI [31] | 2018 | Pak J Biol Sci | Caucasian | PCR-RFLP | 74/151 | 26/50 | 36/76 | 12/25 | 88/176 | 60/126 | Yes | |
| Radanova M [32] | 2015 | Lupus | Bulgaria | RT-PCR | 38/185 | 7/12 | 13/58 | 18/105 | 27/82 | 49/268 | Yes | |
| Cao CW [33] | 2012 | Lupus | China | Sequenom Mass Arrays | 748/750 | 119/116 | 373/364 | 250/256 | 611/596 | 873/876 | Yes | |
| Chew CH [34] | 2008 | Hum Biol | Malaysia | PCR-RFLP | 130/130 | 26/24 | 70/69 | 34/37 | 122/117 | 138/143 | Yes | |
| rs292001 | Yu Y [22] | 2018 | Genet Test Mol Biomarkers | China | PCR | 245/245 | 31/22 | 115/123 | 99/100 | 177/167 | 313/323 | Yes |
| Sa P [35] | 2017 | China Journal of Leprosy and Skin Diseases | China | PCR | 111/120 | 14/11 | 45/49 | 52/60 | 73/71 | 149/169 | Yes | |
| Radanova M [32] | 2015 | Lupus | Bulgaria | RT-PCR | 38/185 | 17/75 | 18/94 | 3/16 | 52/244 | 24/126 | Yes | |
| Mosaad YM [36] | 2015 | Clin Exp Immunol | Egypt | PCR-RFLP | 130/208 | 29/75 | 76/110 | 25/23 | 134/260 | 126/156 | Yes | |
| Zervou MI [37] | 2011 | Human Immunology | Turkey | PCR | 158/155 | 43/54 | 81/91 | 34/10 | 167/199 | 149/111 | No | |
| rs631090 | Yu Y [22] | 2018 | Genet Test Mol Biomarkers | China | PCR | 245/245 | 22/10 | 95/67 | 128/168 | 139/87 | 351/403 | Yes |
| Sa P [35] | 2017 | China Journal of Leprosy and Skin Diseases | China | PCR | 111/120 | 10/5 | 58/82 | 43/33 | 78/92 | 144/148 | No | |
| Radanova M [32] | 2015 | Lupus | Bulgaria | RT-PCR | 38/185 | 0/1 | 4/24 | 31/160 | 4/26 | 66/344 | Yes | |
Association of C1q and SLE susceptibility
According to the forest plot in Figure 2 and Table 2, C1q rs631090 was associated with SLE in homozygote model (OR (95% CI): 2.342 (1.239–4.427), p = 0.009) and recessive model (OR (95% CI): 2.281 (1.227–4.239), p = 0.009), but not in the allelic model (OR (95% CI): 1.169 (0.632–2.162), p = 0.618), heterozygous model (OR (95% CI): 0.983 (0.395–2.448), p = 0.970) and dominant model (OR (95% CI): 1.036 (0.418–2.567), p = 0.938). There was no association between C1q rs172378 and rs292001 and SLE in all five genetic models (rs172378 (allelic model: OR (95% CI): 1.071 (0.949–1.210), p = 0.266), homozygous model: OR (95% CI): 1.172 (0.868–1.584), p = 0.301, heterozygous model: OR (95% CI): 1.080 (0.892–1.306), p = 0.432, dominant model: OR (95% CI): 1.100 (0.918–1.317), p = 0.303, recessive model: OR (95% CI): 1.112 (0.863–1.431), p = 0.412); rs292001 (allelic model: OR (95% CI): 0.877 (0.657–1.170), p = 0.373, homozygous model: OR (95% CI): 0.713 (0.320–1.589), p = 0.408, heterozygous model: OR (95% CI): 0.714 (0.448–1.138), p = 0.157, dominant model: OR (95% CI): 0.703 (0.414–1.196), p = 0.194, recessive model: OR (95% CI): 0.927 (0.601–1.430), p = 0.732)) (Figure 2 and Table 2).
Table 2
Pooled OR and 95% CI, test of heterogeneity, Egg’s test and Trim and fill analysis in the indicated gene of C1q with five genetic models using a random model
| Genetic model | SNP | No. of studies | Test of associationa | Test of heterogeneity | Egg’s test | Trim and fill analysisa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | Z | P | Q | P | I2 (%) | T | P | OR (95% CI) | |||
| Allelic model | rs172378 | 5 | 1.071 (0.949–1.210) | 1.11 | 0.266 | 4.00 | 0.407 | 0.0% | 1.42 | 0.251 | 1.032 (0.895–1.190) |
| rs292001 | 5 | 0.877 (0.657–1.170) | 0.89 | 0.373 | 13.74 | 0.008 | 70.9% | 0.30 | 0.786 | 0.877 (0.657–1.170) | |
| rs631090 | 3 | 1.169 (0.632–2.162) | 0.50 | 0.618 | 9.92 | 0.007 | 79.8% | –0.59 | 0.662 | 1.169 (0.632–2.162) | |
| Homozygous model | rs172378 | 5 | 1.172 (0.868–1.584) | 1.04 | 0.301 | 4.44 | 0.350 | 9.8% | 1.06 | 0.368 | 1.172 (0.868–1.584) |
| rs292001 | 5 | 0.713 (0.320–1.589) | 0.83 | 0.408 | 19.04 | 0.001 | 79.0% | –0.02 | 0.988 | 0.713 (0.320–1.589) | |
| rs631090 | 3 | 2.342 (1.239–4.427) | 2.62 | 0.009 | 0.82 | 0.664 | 0.0% | –0.67 | 0.624 | 2.342 (1.239–4.427) | |
| Heterozygous model | rs172378 | 5 | 1.080 (0.892–1.306) | 0.79 | 0.432 | 0.57 | 0.966 | 0.0% | 1.45 | 0.243 | 1.052 (0.878–1.260) |
| rs292001 | 5 | 0.714 (0.448–1.138) | 1.42 | 0.157 | 10.54 | 0.032 | 62.0% | –0.80 | 0.483 | 0.627 (0.396–0.993) | |
| rs631090 | 3 | 0.983 (0.395–2.448) | 0.04 | 0.970 | 12.82 | 0.002 | 84.4% | –0.67 | 0.622 | 0.983 (0.395–2.448) | |
| Dominant model | rs172378 | 5 | 1.100 (0.918–1.317) | 1.03 | 0.303 | 1.66 | 0.798 | 0.0% | 1.43 | 0.249 | 1.057 (0.891–1.253) |
| rs292001 | 5 | 0.703 (0.414–1.196) | 1.30 | 0.194 | 14.82 | 0.005 | 73.0% | –0.88 | 0.444 | 0.607 (0.356–1.034) | |
| rs631090 | 3 | 1.036 (0.418–2.567) | 0.08 | 0.938 | 13.29 | 0.001 | 85.0% | –0.80 | 0.571 | 1.036 (0.418–2.567) | |
| Recessive model | rs172378 | 5 | 1.112 (0.863–1.431) | 0.82 | 0.412 | 4.37 | 0.359 | 8.4% | 1.06 | 0.367 | 1.112 (0.863–1.431) |
| rs292001 | 5 | 0.927 (0.601–1.430) | 0.34 | 0.732 | 10.44 | 0.034 | 61.7% | 1.79 | 0.171 | 0.927 (0.601–1.430) | |
| rs631090 | 3 | 2.281 (1.227–4.239) | 2.61 | 0.009 | 0.03 | 0.985 | 0.0% | –5.34 | 0.118 | 2.281 (1.227–4.239) | |
TSA
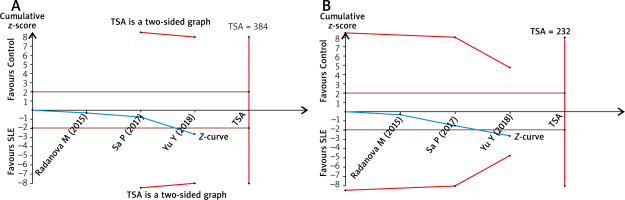
The TSA for the association between C1q rs631090 and overall SLE risk with an overall 5% risk of a type I error, 20% risk of a type II error (power of 80%) and relative risk reduction (RRR) 20% showed that the cumulative z-curve only crossed the traditional boundary but not the trial sequential monitoring boundary and also reached the required information size in the homozygous model and recessive mode (Figure 3). It indicated that it is inconclusive to draw a firm outcome for the association between C1q rs631090 and SLE in the homozygous model and recessive model as more information is needed, thus C1q rs631090 may be a potentially risk factor for SLE.
Publication bias
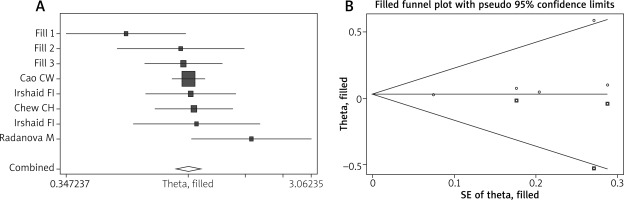
Publication bias was evaluated by both Egg’s test and the trim and fill method. P-values in Egg’s test were all greater than 0.05, suggesting that there was no publication bias in the current meta-analysis (Table 2). Using trim and fill method, the funnel plot is symmetrical after 3 studies are filled and the overall pooled result is no different before and after processing in the allelic model of rs172378 (Table 2 and Figure 4); similar results are obtained in other genetic model of rs172378, rs292001 and rs631090, also indicating that there is no publication bias.
Discussion
The complement system plays a part in both fighting against the invasion of pathogens and regulating the immune system through classical, alternative and lectin pathways. C1q, considered as its important component, makes the activation of the classical complement pathway start following the binding to ligands such as immune complexes, matrix molecules and apoptotic cells. Ultimately, formed membrane attack complex can attack the pathogen involved in innate immunity. However, except for its role in activation of the complement system, C1q is thought to have a direct effect on adaptive immunity. Although, researches had shown that the complement system disorder indeed induced the onset and development of SLE. It can be put down to the anti-inflammatory function of C1q in adaptive immunity. This anti-inflammatory function is to help to solubilize immune complexes in addition to clearance of apoptotic debris [38].
Theoretically, the function of complement in SLE is complex since it may both prevent and exacerbate the disease described as the proverbial “double-edged sword”. On the one hand, tissue insults and end organ damage in SLE patients is due to the excessive activation of the complement pathway. On the other hand, some manifestations of autoimmune diseases such as SLE also can be caused by the deficiencies of certain components of complement pathways [39]. Obviously, C1q as an important component of the complement system faces this question inevitably. Nevertheless, studies have shown that in the absence of this protein among animals and humans, apoptotic debris accumulates and triggers autoimmunity, suggesting that deficiency of C1q is considered to be a strong susceptibility factor for SLE as evidenced by the fact that almost all (≥ 92%) of the known patients with C1q deficiency have developed the disease [32] and frequency of SLE disease is 95% for all patients with C1q deficiency. It is consistent with the ‘waste-disposal’ hypothesis.
Polymorphisms in the complement C1q gene have been reported to be associated with several types of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [40], type 2 diabetes mellitus [41], autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD) [42], and SLE. Nevertheless, the exact mechanism of C1q involvement in SLE pathogenesis is not known. In the present study, we aimed to assess the associations of C1q gene polymorphisms with SLE susceptibility. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis to clarify the roles of C1q gene SNPs in SLE susceptibility. The pooled results showed that C1q rs631090 CC was a risk factor for SLE and there was no association between C1q rs172378 and rs292001 and SLE. In accordance with this result, Martens et al. found that rs631090 was moderately associated with low serum C1q levels [21]. However, TSA indicated that more information is needed to clarify this issue. No relevant between C1q rs172378 and rs 292001 and SLE may be due to that they are located in the noncoding region of C1q gene which does not influence on the production of relevant proteins. The mutation of C1q rs631090 located at the coding region leads to the change of C1q protein, coinciding with the lower level of C1q in SLE patients but anti-C1q was higher.
Although we have worked hard to make the current meta-analysis perfectly, some insufficient aspects can hardly be avoided. Firstly, the sample sizes are small because of the relatively rare related studies. Secondly, stratification analysis is not conducted for the small number of included studies. Thirdly, some sites in the C1q gene are not included in this study because there less than 3 relevant articles. Finally, further investigation should be done to deal with the question of small sample size, ethnic differences, genetic linkage and phenotypic heterogeneity and get more accurate relationship between C1q gene polymorphisms and SLE susceptibility.