Introduction
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is a common hair loss disorder with a progressive miniaturization of the hair follicle leading to vellus transformation of terminal hair [1]. Its prevalence depends on age and race. About 30% of white men will have AGA by the age of 30, up to 50% by 50, and 80% by 70. Chinese, Japanese, and African American people are less affected than Caucasians [2–5]. It is an immune-mediated hair loss disorder, with the following feature: the sudden appearance of hair loss areas on the scalp and other hair-bearing regions.
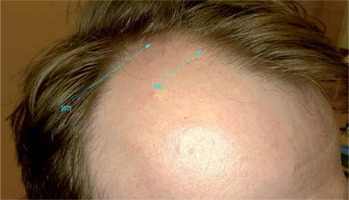
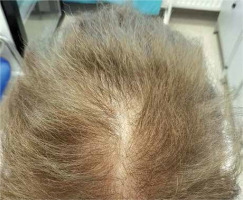
In men, hair loss typically involves the temporal and vertex region (Figures 1, 2). There may be also vertex hair thinning. The occipital area is usually preserved and we can observe the characteristic “horseshoe” pattern [6, 7]. In women, there is Ludwig pattern AGA, with diffuse thinning of the crown region and maintenance of the frontal hairline (Ludwig pattern AGA) [8]. The second type in women is hair thinning limited to the mid-frontal scalp (Olsen type), also referred to as the frontal accentuation or ”Christmas tree-type” pattern [9] (Figure 3).
Figure 2
Androgenetic alopecia in a man. The temporal hair loss. Trichoscopy, 20× zoom, Department of Dermatology, Katowice
There are multiple elements affecting AGA development, such as endocrine abnormality, genetic issue, infection, and psychological/psychiatric diseases [10]. In premenopausal women, AGA can be a sign of hyperandrogenism, along with hirsutism and acnes [8].
To establish the diagnosis of male AGA, a well-taken medical history and clinical assessment is sufficient in the majority of cases. As for women, an AGA clinical assessment and medical history should be complemented by trichoscopy, and in some cases, by laboratory tests, trichogram or even histopathological evaluation of scalp biopsy specimens [9].
AGA can have negative consequences on the patients’ quality of life and may also lead to depression, self-abasement, changed self-image, and fewer and less pleasant social activities. For this reason, it is really important for many patients to receive treatment [11].
Nowadays, topical minoxidil is the only external treatment in men and women and it is also the most popular drug used for the treatment of AGA [12–14].
The second drug approved for AGA treatment is oral finasteride, which can be used only in male patients. It is a selective 5α-reductase inhibitor and is administered orally in a dose of 1 mg once daily [15, 16]; long-term treatment leads to sustained improvement [17–20]. Other doses and treatments are used off-label, however in the majority of cases they are based on well-documented medical knowledge.
Topical minoxidil treatment
The most widely used pharmaceutical treatment of AGA and the only FDA-approved medication for the treatment of female androgenetic alopecia (FAGA) is topical minoxidil [12, 21]. It has been confirmed to induce hair regrowth in AGA patients through vasodilatation. Minoxidil is a pro-drug requiring bio-activation into minoxidil sulfate. The enzyme that catalyses this reaction in the hair follicle is minoxidil sulfotransferase (SULT1A1) (Figure 4).
Figure 4
SULT1A1 catalyzed sulfation of minoxidil. References: Goren A, McCoy J, Lotti TM Prodrugs. In: European Handbook of Dermatological Treatments. Katsambas AD, Lotti TM, Dessinioti C, D’Erme AM (eds.) Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 2015
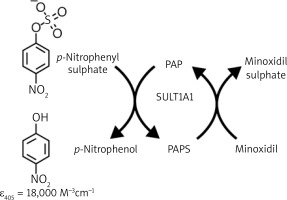
It is hypothesized that SULT1A1 enzyme activity in the hair follicle correlates with minoxidil response for the treatment of AGA [22, 23]. The expression of sulfotransferase in the scalp varies greatly between individuals, and this difference in expression explains the varied clinical response to topical minoxidil treatment [24].
There are two forms of this treatment – 5% and 2% minoxidil. In men, 5% minoxidil is typically used once or twice a day. In women, 2% bminoxidil used twice a day produces a beneficial therapeutic effect comparable to the treatment with 5% minoxidil once a day [25].
The risk of adverse events with both 2% and 5% minoxidil is low. However, some of them have been reported, such as irritant dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, hypertrichosis and cardiac events [26, 27]. Another potential transient adverse effect of using minoxidil is sudden telogen effluvium. It can occur between 6 and 8 weeks after initiation of minoxidil treatment and resolve after a few weeks or months of continued therapy. An episode of telogen effluvium may also occur 3 months after the completion of treatment [9]. Furthermore, interruption of topical minoxidil is followed by increased hair loss. It is also not recommended to use topical minoxidil during pregnancy and lactation, due to the insufficient number of researches during this period [28].
Various clinical researches show that 5% minoxidil has better efficacy than 2% minoxidil. It is based on the average change in non-vellus hair count [29]. Olsen et al. performed clinical studies in men, where using 5% minoxidil contributed to hair growth in approximately 40% of patients [21, 30]. On the other hand, the response to 2% minoxidil is lower. Meta-analysis of several studies reporting the number of responders to 2% minoxidil monotherapy indicates moderate hair regrowth in only 13–20% of female patients [22].
There are some trials of using higher concentrations of topical minoxidil and it seems to be effective in up to 60% of non-responders, but for this moment, it remains an off-label treatment [31].
A biomarker for predicting treatment response would have significant clinical utility due to the prolonged treatment time required to elicit a therapeutic response (used daily for a period of 3–6 months) combined with the variable efficacy of minoxidil in the general population [13, 22].
Sulfotransferase activity
Sulfotransferases are xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes with the highest expression found in the human liver [32], but hair follicle cells also express it [13, 22, 30]. The correlation between SULT1A1 expression in the scalp and minoxidil response has been previously reported [33]. Frame et al. have adapted a colorimetric assay of SULT1A1 activity to measure the conversion of minoxidil in the hair root of a plucked human hair [34]. The expression of SULT1A1 has been localized in the outer root sheet [30]. In the assay, the conversion of minoxidil to minoxidil sulfate is coupled with the conversion of p-nitrophenyl sulfate to p-nitrophenyl, which can be quantified by optical absorbance at 405 nm.
In another study, Goren et al. tabulated the data based on sulfotransferase activity (optical density at 405 nm). They chose a cut-off value of less than 0.4 OD 405 as a marker for low follicular sulfotransferase activity. Based on the 0.4 OD 405 marker, their assay was able to predict responders to minoxidil therapy with a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 73%. Their results support sulfotransferase activity in the hair follicle as a strong predictor of minoxidil response in AGA patients [13].
On the other hand, Roberts et al. observed that women with a score slightly above the cut-off value of 0.4 AU exhibited only minor improvements in hair growth compared with women with scores over 0.6 AU. This would suggest that there may be a continuum of minoxidil response directly proportional to sulfotransferase activity in the hair follicle. Extending this logic, this finding implies that upregulation of sulfotransferase could potentially be an effective adjunctive therapy to topical minoxidil [22].
Sulfotransferase activity can be modulated by various compounds. In the human liver it is significantly inhibited by salicylic acid. It is suspected that oral aspirin inhibits sulfotransferase activity in hair follicles, potentially affecting minoxidil response in AGA patients. Goren et al. determined the follicular sulfotransferase enzymatic activity following 14 days of oral aspirin administration. In their cohort of 24 subjects, 50% were initially predicted to be responders to minoxidil. However, following 14 days of aspirin administration, only 27% of the subjects were predicted to respond to topical minoxidil [35].
Sharma et al. carried out another noteworthy study, namely they elucidated the mechanism of increasing minoxidil response by retinoids. They demonstrated that topical tretinoin application influences the expression of follicular sulfotransferase. Of clinical significance, in their cohort, 43% of subjects initially predicted to be nonresponders to minoxidil were converted to responders following 5 days of topical tretinoin application [36].
Retrospective studies are very limited and a larger prospective study is necessary to further validate the novel assay. Many compounds have been reported to upregulate sulfotransferases in the liver [37, 38]. It is now important to find novel compounds modulating sulfotransferase activity in the scalp. Then, the SULT1A1 activity assay would be a valuable tool for dermatologists to achieve permanent effects of AGA treatment [13].
Other forms of treatment
Oral minoxidil
In one study, oral minoxidil at a dose of 5 mg/day in men led to an increased hair count; however, the increase is only slightly higher compared to studies investigating topical minoxidil. Side‐effects of oral minoxidil included hypertrichosis (93%), pedal oedema (10%) and ECG alteration (10%) [39, 40].
Topical finasteride
Nowadays, concern about influence of oral finasteride on fertility has increased among patients [20]. Patients often seek consultations to avoid finasteride and research different treatments, even if they are told about the well-established efficacy of finasteride.
Some recent studies with topical finasteride formulations have been published. A double-blind study showed that the therapeutic effects of 1% finasteride gel applied twice daily and oral finasteride, 1 mg daily, were relatively similar (evidence level 1+) [41]. Relatedly, topical finasteride can be considered for hair density maintenance after initial improvement with oral finasteride, thereby avoiding the need for using oral finasteride indefinitely [42].
Dutasteride
Like finasteride, dutasteride is now becoming a popular off-label treatment option in AGA. It inhibits both type I and type II 5α-reductase and it was shown to be more efficacious than finasteride with comparable adverse effects. Therefore, dutasteride could become a treatment of choice for AGA in the near future [43–46]. Phase II and III trials in men with AGA have shown dose-dependent (0.5 mg/day and higher) efficacy of the drug assessed at 12 and 24 weeks of treatment. The dose-dependent response to treatment was correlated with decreased DHT activity in the scalp. It is important that women of reproductive age should use effective contraception during dutasteride treatment and 6 months after the termination of therapy, mainly due to the possible risk of feminization of male foetuses [9].
Mesotherapy with dutasteride
Also mesotherapy with dutasteride may be an effective therapy for patients with AGA even with less intensive treatment schedules, as sessions once every 3 months [47].
Spironolactone
It is the most commonly used off-label anti-androgen for the treatment of FAGA. Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic and a structural antagonist of aldosterone. In the treatment of AGA, it acts by decreasing the production and competitively blocking the androgen receptor in the target tissue. It has been used to treat FAGA at a dose of 50–200 mg daily for at least 6 months [26, 48, 49].
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is an antifungal used topically as a 2% shampoo, which results in increased hair growth in FAGA. Ketoconazole also has antiandrogenic properties as it can interfere with steroidogenesis. Its use in combination with oral finasteride 1 mg might produce an additional decrease in scalp DHT levels [50, 51].
Prostaglandin analogues
Elongation and pigmentation of eyelashes and eyebrows was observed as a side effect in patients using the topical prostaglandin F2 (PGF2) analog latanoprost for glaucoma treatment. This effect is apparently due to prolongation of the anagen phase [52, 53].
Garza et al. observed that PGD2 and its synthetase are highly expressed in the scalp of men with AGA [54]. They also reported that high levels of PGD2 induced miniaturization, sebaceous gland hyperplasia, and alopecia in mice and that topical PGD2 inhibited hair growth in the application area in mice. In addition, they showed that levels of PGE2, which is a hair growth promoter, are higher in normal scalp than in AGA scalp. Furthermore, they reported that the PGD2 receptor, known as GPCR44, is a potential target for treatments. Setipiprant, a selective oral antagonist to the PGD2 receptor, will possibly be developed for this indication [54, 55].
Cyproterone acetate
There is limited evidence that oral cyproterone acetate may be helpful in women with AGA and hyperandrogenism. Side‐effects of this medicine include depressive mood changes and liver toxicity. There is an increased risk of venous thromboembolism in patients taking oestrogen‐containing oral contraceptives, which may be greater in those taking cyproterone acetate than other oral contraceptives [28].
Flutamide
Flutamide is a nonsteroidal selective antiandrogen that acts by inhibiting the binding of endogenous androgens to their receptors. In the light of limited data on the efficacy and safety profile of the drug, there are currently no grounds to recommend flutamide for the therapy of FAGA [9, 56].
Oestrogens
There are no studies that would validate the use of oestrogens, orally or topically, in the therapy of AGA [9, 28].
Platelet-rich plasma
An alternative method of treatment can be platelet-rich plasma (PRP), an autologous form of treatment, which is a new option for patients who do not want to take medicaments [57]. It is recommended that 3 monthly sessions of PRP (once monthly × 3 treatments) be used followed by a 3- to 6-month maintenance period [58].
Microneedling
Existing literature data are insufficient to recommend microneedling as a therapeutic method in male or female androgenetic alopecia [9].
Light and laser therapy
Light or laser therapy with various wavelengths is also being applied in AGA treatment. Akiko Ohtsuki et al. reported that a 308 nm excimer lamp could induce the effective regrowth of hair in AGA patients without causing serious side effects, especially in the cases with a single lesion [59, 60]. In 2010 Yoo et al. reported that in a patient with a single AGA lesion treated by a fractional photothermolysis laser, hair growth could be observed after 1 month of treatment and complete regrowth in all lesions without any side effects were obtained after 6 months of laser therapy [61]. However, there has been a limited study about the effects of fractional laser treatment on AGA. Therefore, the efficacy and safety of a non-ablative fractional (NAF) laser combined with topical minoxidil treatment were evaluated in AGA patients in Wuyuntana Wang's study [62].
A combined treatment with NAF 1550-nm laser and topical minoxidil may be a good therapeutic alternative for patients with AGA as well as alopecia universalis and totalis without systemic and local side effects [62].
JAK–STAT signalling
Pharmacologic inhibition of the Janus kinase (JAK)–STAT pathway can induce hair regrowth in alopecia areata in humans. Harel et al. reported that the topical use of JAK–STAT inhibitors promoted anagen growth in normal hair follicles in humans. These findings reveal new perspectives to be explored regarding the efficacy of JAK inhibitors in AGA [63, 64].
Melatonin
Topical application of melatonin 0.1 % solution was shown to significantly increase anagen hair in men and women AGA in two controlled studies, with good tolerability [48, 65, 66].
Botulinum toxin
It is currently regarded as an experimental method with insufficiently proven efficacy [67, 68].
Other modalities
Nowadays, alternative treatments are more and more common including vitamin, mineral and herbal components suggested for management of androgenic alopecia and this has increased global demand [69].
Surgical treatment
Hairless areas can be permanently covered again cosmetically, albeit with a decreased density. Hair restoration surgery involves scalp reduction surgery, hair transplantation or a combination of both. Over the last decades, hair transplantation has evolved into a microsurgical procedure. Follicular units of 1–4 hairs are transplanted in large numbers and high densities [28, 29]. However, there are no randomized controlled studies comparing hair transplantation vs. no hair transplantation [28]. A summary of possible therapeutic options in AGA is presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Summary of alternative therapeutic options in androgenetic alopecia
| Citied study | Alternative method of AGA treatment |
|---|---|
| Lueangarun et al. (2015) [39] Ramos et al. (2020) [40] | Oral minoxidil |
| Fertig et al. (2017) [20] Hajheydari et al. (2009) [41] Chandrashekar et al. (2015) [42] | Topical finasteride |
| Arif et al. (2017) [43] Eun et al. (2010) [44] Azzouni et al. (2012) [45] Shanshanwal et al. (2017) [46] Brzezińska-Wcisło et al. (2018) [9] | Dutasteride |
| Saceda-Corralo [47] | Mesotherapy with dutasteride |
| Varothai et al. (2014) [48] van Zuuren et al. (2012) [26] Atanaskova Mesinkovska et al. (2013) [49] | Spironolactone |
| Inui et al. (2007) [50] Perez (2004) [51] | Ketoconazole |
| Sasaki et al. (2005) [52] Tauchi et al. (2010) [53] Garza et al. (2012) [54] Nieves et al. (2014) [55] | Prostaglandin analogues |
| Kanti et al. (2018) [28] | Cyproterone acetate |
| Brzezińska-Wcisło et al. (2018) [9] Kelly et al. (2016) [56] | Flutamide |
| Brzezińska-Wcisło et al. (2018) [9] Kanti et al. (2018) [28] | Oestrogens |
| Santos et al. (2019) [57] Gupta et al. (2019) [58] | Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) |
| Ohtuski et al. (2010, 2013) [59, 60] Yoo et al. (2010) [61] Wuyuntana Wang et al. (2019) [62] | Light or laser therapy: |
| Xing et al. (2014) [63] Harel et al. (2015) [64] | JAK-STAT signalling |
| Varothai et al. (2014) [48] Fischer et al. (2004, 2012) [65, 66] | Melatonin |
| Carloni et al. (2020) [67] Shon et al. (2020) [68] | Botulinum toxin |
| Asnaashari et al. (2020) [69] | Vitamin, minerals, herbal medicines |
| Kanti et al. (2018) [28] Brzezińska-Wcisło et al. (2018) [9] | Surgical treatment |
Conclusions
Androgenetic alopecia is the most prevalent form of hair loss in men and women. Currently, the main Food and Drug Administration-approved AGA treatments are topical minoxidil and oral finasteride. Previously, it was demonstrated that topical minoxidil was metabolized to its active metabolite, minoxidil sulfate, by sulfotransferase enzymes located in the outer root sheath of hair follicles. It is hypothesized that SULT1A1 enzyme activity in the hair follicle correlates with minoxidil response for the treatment of AGA. It is now important to find novel compounds modulating sulfotransferase activity in the scalp. Then, the SULT1A1 activity assay would be a valuable tool for dermatologists to achieve permanent effects of AGA treatment.