Introduction
According to current standards for health professions, physiotherapists and nursing staff are separate professional groups [1]. This means that each of them has Their own role in the therapeutic team, and their duties are defined by the acts on these professions, respectively the Act on the Profession of Physiotherapist of 15 September 2015 [2] and the Act on the Professions of Nurses and Midwives of 15 July 2011 [3]. Although the individual medical professions for which laws regulating their functioning have been passed are independent professions, due to The specificity of their work they are mutually dependent on each other. In addition, the shortage of professionals in medical care is growing year by year, which increases the risk of overlapping competences as a result of a lack of adequate staff.
The aim of the study was to analyze the factors influencing the quality of cooperation with a physiotherapist in the opinion of nursing staff working in hospital facilities. An additional objective was to assess the role of The physiotherapist in The medical team by defining his or her responsibilities in the therapeutic process from the point of view of the representatives of the nursing community.
Material and methods
The study involved 355 nursing personel (including 342 women and 13 men) working in county, provincial or national hospitals and various levels of referral. The study used the method of purposive sampling. The tool used was the author’s questionnaire, which was given to the respondents personally in paper form. The questionnaire included metric questions, questions about cooperation with a physiotherapist in the therapeutic team and about the scope of responsibilities of this professional group. The written consent of the directors of the hospitals covered by the study and the respondents themselves was obtained to conduct the study.
The statistical analysis was performed in MS EXCEL 2016 and SPSS Statistics spreadsheet software, the results were presented using basic statistical tools, the significance level p<0,05.
Results
A total of 355 respondents took part in the survey. The study group was characterized by gender, age, seniority and hospital ward in which they were employed. Women constituted the vast majority of the study group (96%), and more than 3/4 (78%) were over 40 years old. As many as 80% of the surveyed representatives of nursing staff had worked in the profession for 10 years or more. The largest group were employees of internal medicine and orthopaedics departments. The distribution of respondents’ responses is shown in Table 1.
Table 1
Characteristics of the study group N=355.
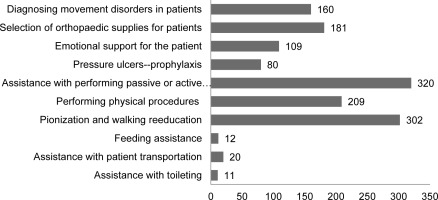
The main duties of a physiotherapist in the therapeutic team were: active and passive physical rehabilitation, patient verticalization and gait training, as well as using physical therapy modalities. Duties such as helping to toilet the patient and helping to feed the patient were less frequently chosen (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The scope of duties of a physiotherapist in the therapeutic team according to the nursing staff examined.
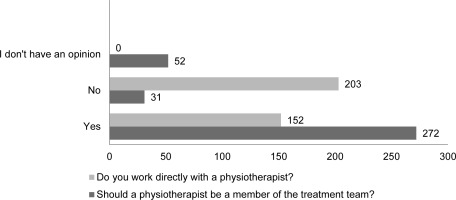
A significant majority (77%) of respondents believed that a physiotherapist should be a member of the treatment team. However, less than half of the respondents (43%) declared direct cooperation with a physiotherapist, despite the fact that physiotherapists are employed in all the surveyed facilities (Figure 2).
Figure 2
Distribution of responses declaring direct cooperation with a physiotherapist or lack of it and opinion on the presence of a physiotherapist in the therapeutic team.
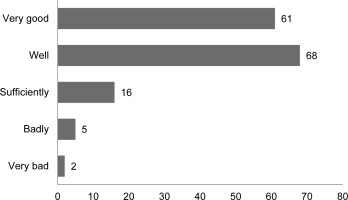
Nursing staff working directly with the physiotherapist were asked to evaluate this cooperation. More than 84 % (129) of respondents rated this cooperation as very good and good (Figure 3).
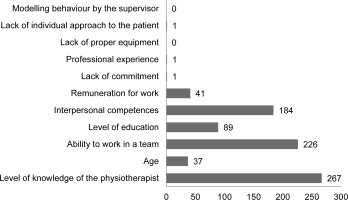
The respondents were also asked to indicate the factors which, in their opinion, affect the cooperation between the nursing staff and the physiotherapist. According to the respondents, the most important factors include: the level of knowledge of the physiotherapist, the ability to work in a team and interpersonal competences. None of the respondents indicated that the problem in cooperation is due to the lack of appropriate equipment or behavioural modelling by the supervisor (Figure 4).
Figure 4
Factors influencing the quality of cooperation with a physiotherapist in the opinion of the respondents.
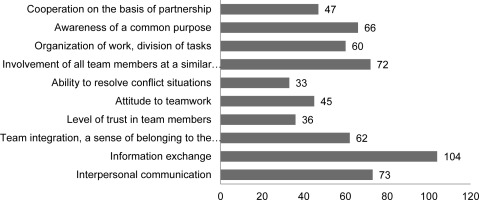
Nearly half of the respondents indicated the need to conduct educational activities in the field of cooperation between members of the therapeutic team. On the other hand, each of them indicated the elements which, in their opinion, should be improved in order to improve the work of the therapeutic team. The nursing staff paid attention to factors such as: exchange of information, interpersonal communication, involvement of all team members on an equal level, as well as awareness of a common goal, team integration and organization of work (Figure 5).
Discussion
The basic therapeutic team providing health services in hospital facilities consists of a doctor, nurse, physiotherapist and psychologist. Of course, depending on the specifics of the facility, this team may be supplemented with other specialists, e.g. speech therapist, occupational therapist, dietician, etc. [4]. All members of the interdisciplinary team are partners in the therapeutic process. What is more, in the current development of medical and social sciences, cooperation between representatives of various medical professions is the foundation of modern health care systems [5], where the paternalistic model, focused on the needs of medical professionals, is being abandoned and the biopsychosocial model, characterized by a holistic approach to the needs of the patient, is applied [6]. When the main task of the therapeutic team is to act for the benefit of the patient on many levels simultaneously, strong and continuous cooperation between medical professionals is essential. In addition, there are already studies confirming the impact of communication and cooperation between doctors and nurses on the quality of medical services [7, 8]. So far, however, there is a lack of scientific reports showing how the role of a physiotherapist in a therapeutic team is perceived by representatives of other medical professions. As one of the most common types of interaction between staff in hospitals is between physiotherapists and nursing staff, this study was conducted to find out the opinions of nurses on this topic and to determine the factors influencing the cooperation of these two professional groups.
Nurses and physiotherapists are one of the largest groups in terms of the number of medical staff in Poland [1]. That is why in hospital facilities there is most often interaction between representatives of these professions. Taking into account the ongoing demographic adverse phenomena, the increase in demand for medical care, limited human resources and the complexity of needs in health care, it is very important for specialists from various fields to cooperate with specialists in various fields and to allocate resources wisely. All the more so because the average age of representatives of these professions in hospital facilities is the highest. This means that hospitals providing universal access to health care employ the oldest group of physiotherapists, and there are no colleagues willing to replace retiring colleagues [9]. The situation is similar with nursing staff. Which, in a way, is reflected in our research. (The average age of the respondents was over 40 years in 78% of cases.)
Both the profession of physiotherapist and nurse is regulated by statute and is subject to clearly defined rules for obtaining the right to practise the profession and to practise the profession as well as professional liability. The Act on the Profession of Physiotherapist came into force on 15 July 2015, so 8 years have passed since then. This document has raised the profile of the physiotherapy profession in society, but also in the medical community. This is also confirmed by the conducted study, which verified the knowledge of the scope of duties by the nursing staff. The vast majority of respondents correctly indicated the scope of duties of a physiotherapist. The most frequently indicated were active and passive physical rehabilitation, verticalization and gait re-education, as well as physical procedures. This is in accordance with the provisions of the Act on the Profession of Physiotherapist [2].
There are few publications available in the Polish literature on therapeutic teams and the evaluation of their cooperation. An interesting study among physiotherapists and nursing staff was conducted by Salamon and Mortar in 2007. The authors have shown that there is a shortage of several specialists in the therapeutic teams studied, which means that other members (especially nurses and physiotherapists) are forced to perform additional activities [10]. The shortage of staff may explain why, in the opinion of some nursing staff, the physiotherapist’s duties include helping with feeding and toileting the patient, or transporting them to examinations. However, these activities are not included in the scope of duties under the Act on the Profession of Physiotherapist [2].
It is also worth noting that representatives of the nursing community declaring direct cooperation with a physiotherapist in over 84% of cases assess this cooperation positively (good and very good). Similar results were obtained in another study, where 82% of respondents (mainly physiotherapists and nurses) had no objections to effective cooperation in their team [10].
The collaboration between physiotherapists and nursing staff is complex and can be influenced by many factors. According to literature reports, the three most common determinants influencing cooperation between representatives of medical professions are: the scope of responsibilities and roles in the team, the degree of communication, trust and respect for the other profession that team members have for each other, and education in this area [11]. Meanwhile, in the opinion of nursing staff, the main factors influencing the cooperation between a physiotherapist and a nurse are the level of knowledge of the physiotherapist, the ability to work in a team and interpersonal competences. Therefore, it can be assumed that the ranges of the mentioned determinants are similar, referring to the level of knowledge and soft skills. Physiotherapists and nursing staff, as team members, should be aware of each other’s roles and the importance of meeting, talking and communicating together. This approach can be useful in distributing work evenly, making patient care more efficient as a result.
In practice, the implementation of cooperation between representatives of different medical professions can be difficult. Therefore, it seems necessary to implement clear regulations that clearly define the areas of cooperation while respecting the autonomy of individual medical professions and allow for a transparent definition of where the legal and deontological responsibility of each group begins and ends. On the other hand, the central position of the patient and the common goal of improving the patient›s well-being remain unchanged, because this is how we should perceive health according to the WHO [13].
The benefits of good communication and cooperation between members of the therapeutic team, including physiotherapists and representatives of the nursing community, may not only result in a much better quality of health care, but also, from an economic point of view, result in a better use of time for the patient and significantly reduce the costs associated with the ineffective phenomenon of shifting responsibility for the patient [5].
Only proper organization of the therapeutic team, whose work is a complex process, enables comprehensive patient care, contributes to minimizing costs and leads to an increase in the quality of patient care [12]. Many studies have shown that the lack of good organization of team work and poor communication between its members can prolong the treatment process, and factors such as efficient leadership, good communication and coordination in the team, care for the cohesion and quality of team work, as well as a friendly work environment have a positive impact on the entire treatment and patient care process [5, 7, 12].
The key to success in promoting the role of a physiotherapist in the therapeutic team, in the opinion of the respondents, is education. Every second respondent pointed to the need to conduct educational activities in the field of cooperation between members of the medical team. Similar recommendations can be found in other publications [14]. Importantly, this education should not be limited only to medical issues, but should also include «soft» skills and the art of effective communication. Interestingly, in the conducted study, the nursing staff indicated the need to improve such factors as: information exchange, interpersonal communication, involvement of all members of the medical team at an equal level, awareness of a common goal, team integration and work organization.
Conclusions
This study has shown that the implementation of the Act on the Profession of Physiotherapist into the Polish legal system is only the beginning of the process facilitating cooperation between members of interdisciplinary therapeutic teams in practice. Education turns out to be irreplaceable. As the results show, it is worth educating nursing staff in order to improve the therapeutic process and improve the effectiveness of communication between medical care employees, including between the physiotherapist and the nurse. Such education should concern not only the medical aspects, but also the details defining the place and role of each medical professional who provides care to patients. The main areas of training should include: the ability to work in a team, the principles of good communication, the development of soft skills and knowledge of the roles of team members related to the specifics of the tasks performed (defining competences and responsibilities). Only by learning how to work together can representatives of medical professions effectively improve the quality of the health care system. And at the end of the day, it’s all about working together for the good of the patient. Because both professional groups have the same goals, only that they achieve them with different tools.
Recomendations for practice
The dynamic development of medicine is driving the trend towards the creation of complex therapeutic teams. It is impossible to provide complete care to a patient without dividing work and competences among individual employees of the health care system. Therefore, the education of medical staff based on the implementation of the basics of work in therapeutic teams will have a positive impact on the therapeutic process, which will translate into benefits for both patients and medical care professionals. According to the research, it seems to be valuable to define professional competences precisely, respecting the autonomy of individual professions and emphasizing cooperation between representatives of medical professions.

 POLSKI
POLSKI